I'm currently working on a sentiment analysis problem that requires me to collect big data from Twitter and process it for later. As a first step, I thought it would be helpful to simply grab a single Tweet and study its structure. Here is a very simple way to get data from Twitter's API and write it to a file so that you can study it's internal workings using Twitter gem and Rails Console.
This entry will show you how to publish either to JSON or to YAML.
Step 1 - Create a rails app
If you don't know how to create a rails app, here's a quick tutorial. Here's my simple command.
rails _5.0.0_ new my_api_app --api
Change directory into your rails app.
cd my_api_app
Step 2 - Install Twitter Gem
Open up your Gemfile and add this line of code to the bottom.
...
# ###
# App Specific Gems
# ###
gem 'twitter', '~> 6.0'
Then run bundle install from within Terminal.
bundle install
Step 3 - Create Twitter API Keys
A. First visit [Twiter Application Management](Create New App) and create a new app.
B. Second, go to Keys and Access Tokens and get:
- Consumer Key (API Key)
- Consumer Secret (API Secret)
- Access Token
- Access Token Secret
Step 4 - Prepare the Twitter API library
Follow the instructions from the Twitter gem and paste the Twitter keys into the API library using your favorite Text Editor.
client = Twitter::REST::Client.new do |config|
config.consumer_key = "YOUR_CONSUMER_KEY"
config.consumer_secret = "YOUR_CONSUMER_SECRET"
config.access_token = "YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN"
config.access_token_secret = "YOUR_ACCESS_SECRET"
end
Step 5 - Start Rails console
rails c
Step 6 - Add Twitter Library
Once you've opened up your Rails console, paste the configuration.
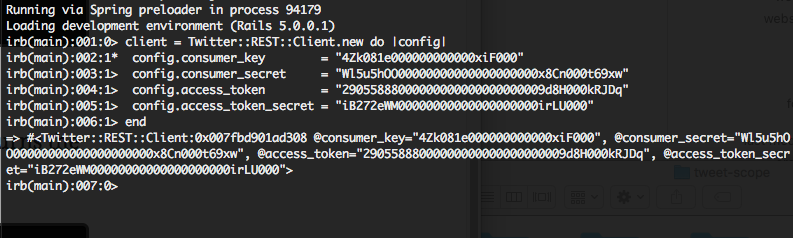
client = Twitter::REST::Client.new do |config|
config.consumer_key = "4Zk081e000000000000xiF000"
config.consumer_secret = "Wl5u5hOO00000000000000000000x8Cn000t69xw"
config.access_token = "29055888000000000000000000009d8H000kRJDq"
config.access_token_secret = "iB272eWM00000000000000000000irLU000"
end
Step 7 - Create a search
This is an example of a Twitter query for the band "stereolab", returns the first result and converts it to JSON format.
search = client.search("#stereolab", count: 1, result_type: "recent", lang: "en").first.to_json
Step 8 - Create a new JSON file
OK, we're at the home stretch. All we need to do is create a file and save the search results to the file.
f = File.new("stereolab_result.json", "w")
Insert the search result into the text file.
f << search
Close the file.
f.close
Step 9 - Create a YAML file
Create a YAML file.
f = File.new("stereolab_result.yaml", "w")
Create the same search with a YAML response.
search = client.search("#stereolab", count: 1, result_type: "recent", lang: "en").first.to_yaml
Insert the result into the text file.
f << search
Close the file
f.close