If you work regularly with MySQL, Mongo DB, AWS RDS, or DynamoDB, then you might find Navicat Premium useful. Navicat Premium helps you create views, queries and functions using an easy-to-use UIX. Even better, you can save your work into the cloud for reuse.
Here's a snapshot of the Navicat UIX. If you look to the left, you'll notice that there are views, queries, and functions.
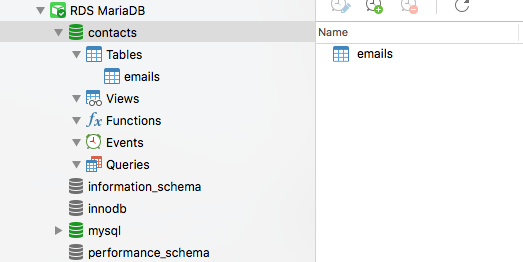
Below are a few of my favorite examples of views, queries and functions.
Navicat - Views
Get Unique Data from a Single Column
Suppose you have a database filled with thousands of rows and one of the columns is titled Cities. You're interested in knowing how many unique cities are within the thousands of observations.
# Create a view that will only show unique values from within a single column.
SELECT DISTINCT `column name` FROM `table name`
Navicat - Queries
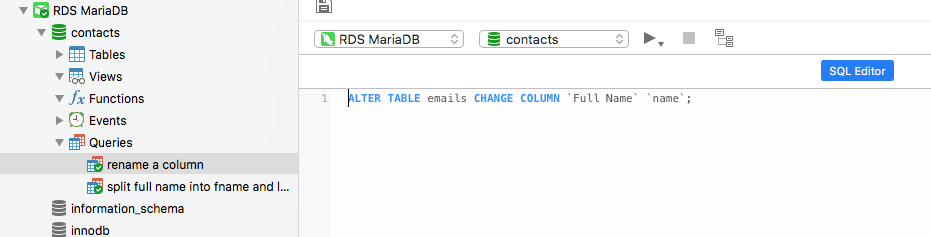
Modify a Column Name
Suppose you just want to change the name of a column, here's how to run that function.
ALTER TABLE MyTable CHANGE COLUMN `Full Name` to `Name`;
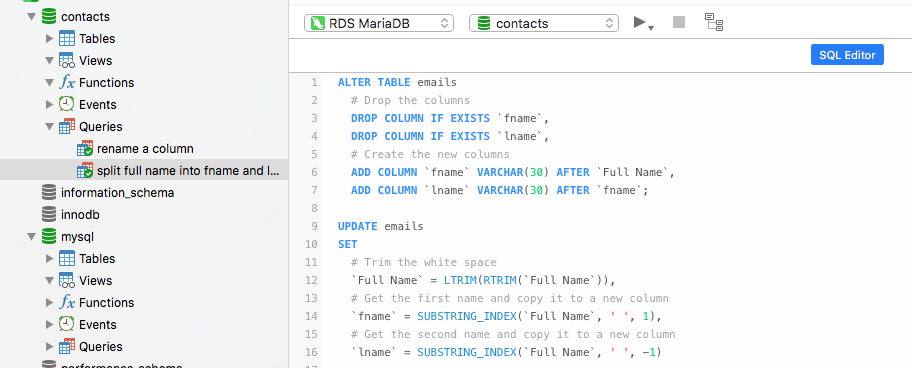
Split Full Name into Fname and Lname
Suppose you have a column titled Full Name and you want to split the information into two columns Fname and Lname. Here's how
ALTER TABLE emails
# Drop the columns
DROP COLUMN IF EXISTS `fname`,
DROP COLUMN IF EXISTS `lname`,
# Create the new columns
ADD COLUMN `fname` VARCHAR(30) AFTER `Full Name`,
ADD COLUMN `lname` VARCHAR(30) AFTER `fname`;
UPDATE emails
SET
# Trim the white space
`Full Name` = LTRIM(RTRIM(`Full Name`)),
# Get the first name and copy it to a new column
`fname` = SUBSTRING_INDEX(`Full Name`, ' ', 1),
# Get the second name and copy it to a new column
`lname` = SUBSTRING_INDEX(`Full Name`, ' ', -1)
Navicat - Functions
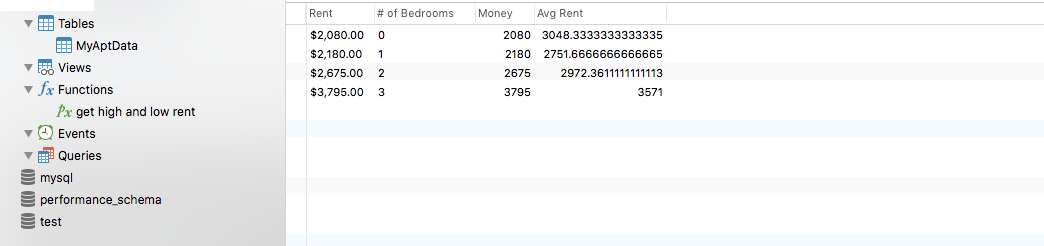
Working with Money
Suppose you're researching apartment rental data and you get a CSV file that contains $ and , symbols inside the column with numerical data.
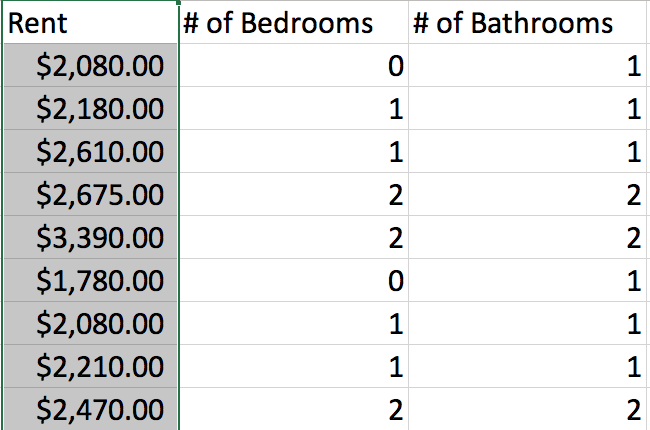
Before you can run any calculations, you'll first need to do a few things such as:
1. Remove the $ and , from the Rent column.
2. Convert the Rent into an Integer.
3. Assign the newly created Integers into a new column called Money.
4. Run a function (such as AVG() to calculate an average.
5. Assign the results from AVG() to a new column called Avg Rent.
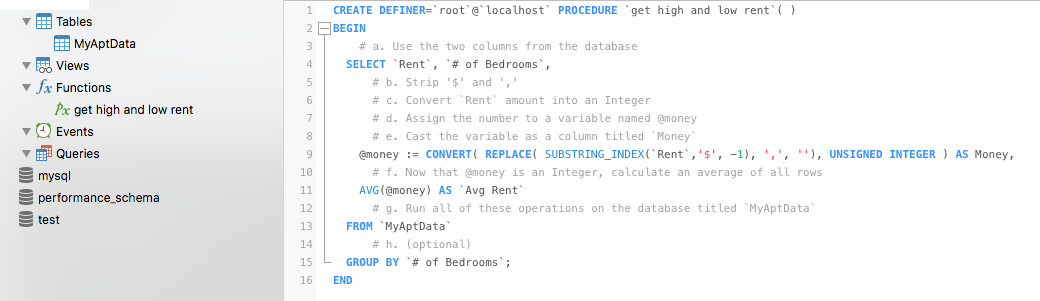
SQL Statement
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `get high and low rent`( )
BEGIN
# a. Use the two columns from the database
SELECT `Rent`, `# of Bedrooms`,
# b. Strip '$' and ','
# c. Convert `Rent` amount into an Integer
# d. Assign the number to a variable named @money
# e. Cast the variable as a column titled `Money`
@money := CONVERT( REPLACE( SUBSTRING_INDEX(`Rent`,'$', -1), ',', ''), UNSIGNED INTEGER ) AS Money,
# f. Now that @money is an Integer, calculate an average of all rows
AVG(@money) AS `Avg Rent`
# g. Run all of these operations on the database titled `MyAptData`
FROM `MyAptData`
# h. (optional)
GROUP BY `# of Bedrooms`;
END
SQL Result
Here's what it will look like in Navicat.